#systemd #linux
[source](https://www.tecmint.com/list-all-running-services-under-systemd-in-linux/)
systemd - system manager and services controller, a replacement for the init process
systemctl - shows all loaded systemd units
#### List of All Units in systemctl
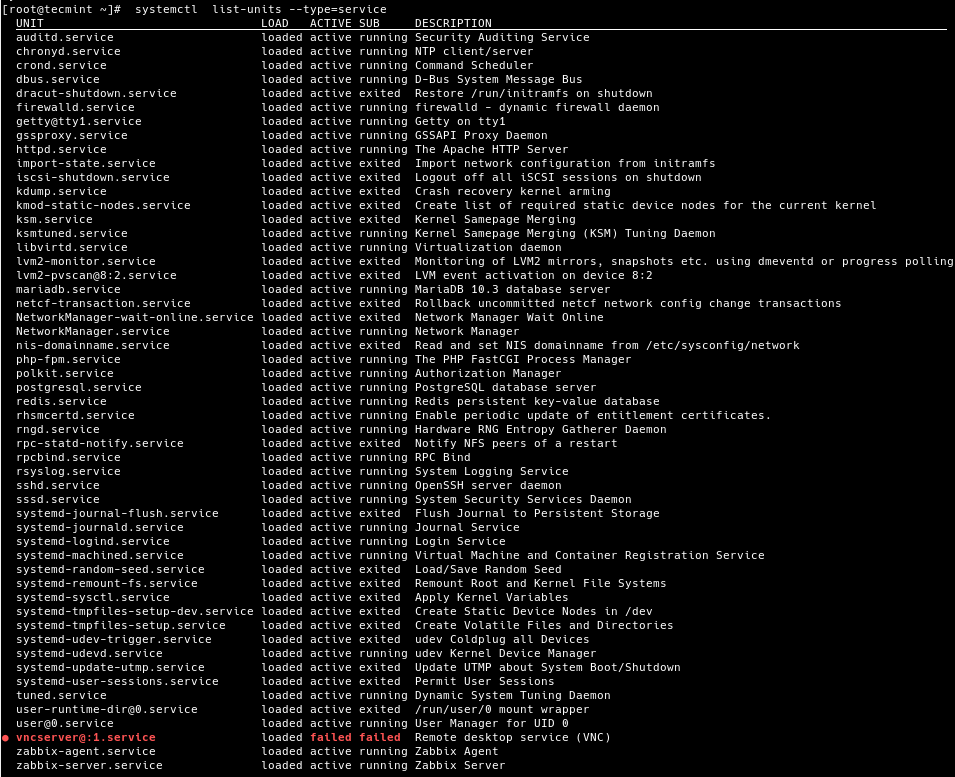
To get a list of all loaded services in your system (regardless of whether they are active, running, disabled, or failed), use the **list-units** subcommand and switch `--type` with the value of service.
```bash
# systemctl list-units --type=service
OR
# systemctl --type=service
```
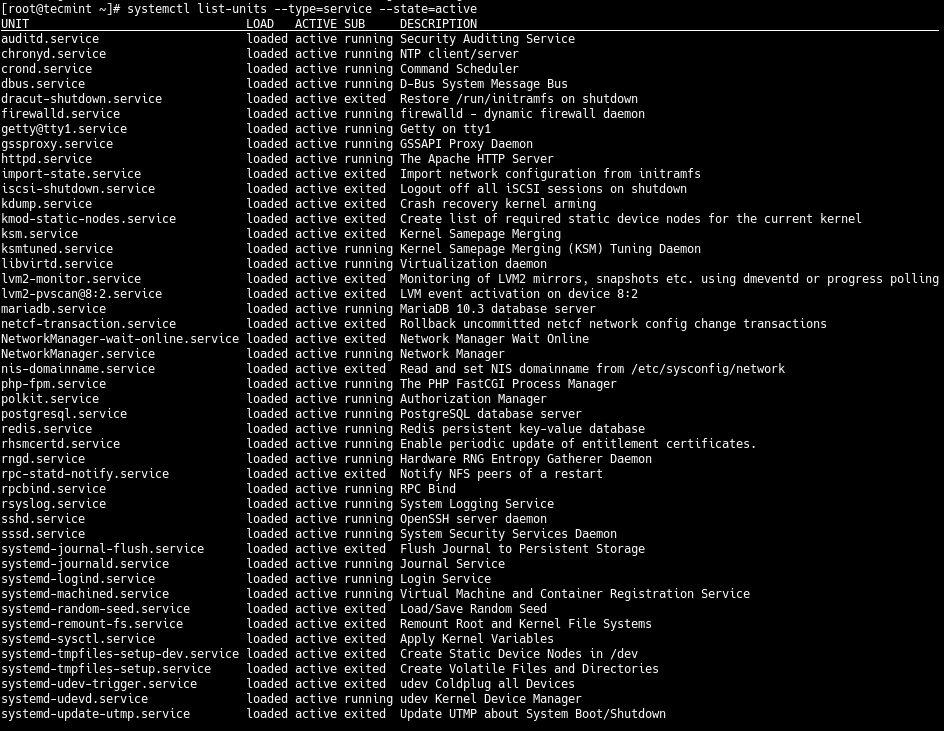
To get a list of all loaded but active services, both running and exited, you can add the `--state` option with the value of **active**, as shown below.
```bash
# systemctl list-units --type=service --state=active
OR
# systemctl --type=service --state=active
```
#### List of Running Services in systemctl
To quickly view all running services (i.e., all loaded and actively running services), execute the following command.
```bash
# systemctl list-units --type=service --state=running
OR
# systemctl --type=service --state=running
```
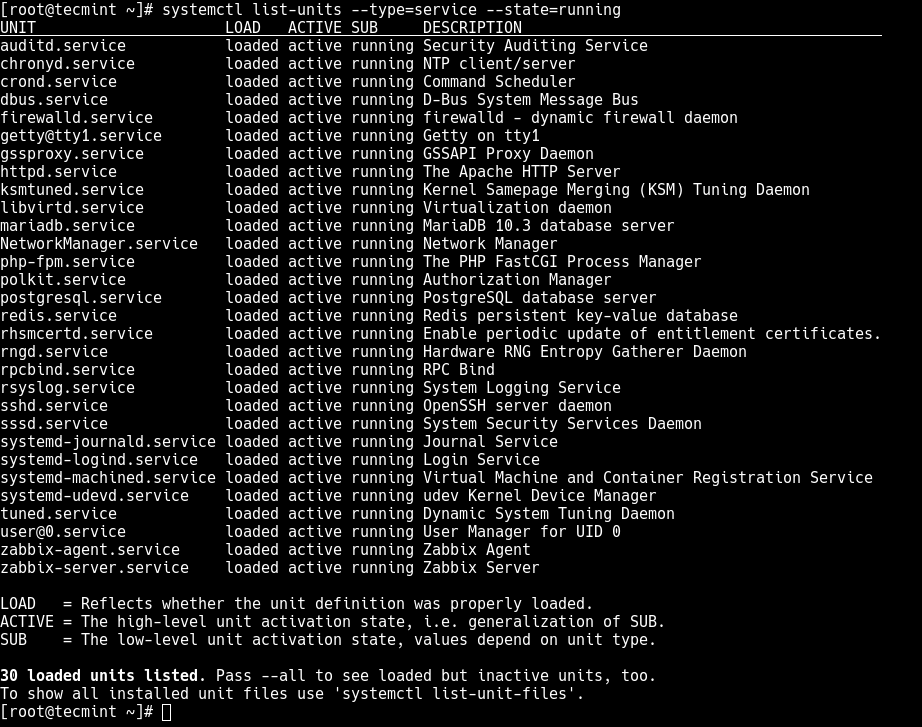
Key terms related to **Systemd** units and their status:
- **Unit** - A unit can be a service, socket, device, or various other entities.
- **Load** - Indicates whether the unit is loaded or not. A unit can be loaded but not necessarily active.
- **Active** - Indicates whether the unit is actively running or if it has encountered issues and is in a failed or inactive state.
- **SUB** - Provides additional information about the specific state of the unit. For services, it may indicate whether the service is running, stopped, or has encountered problems.
- **Description** - Helps users identify and understand the purpose of the unit without delving into detailed configuration files.
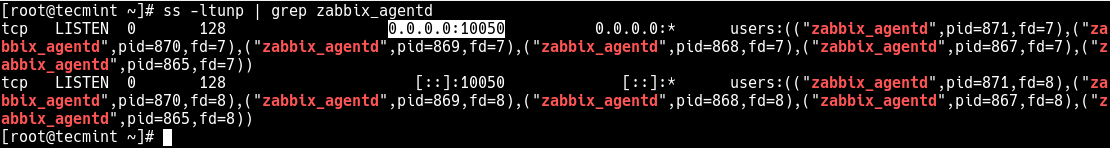
#### Determine the Port on Which a Daemon Process is Listening
**Use the netstat or ss command**
`-l` means to print all listening sockets,
`-t` displays all TCP connections,
`-u` shows all UDP connections,
`-n` means to print numerical port numbers (instead of program names)
`-p` means to show the program name.
```bash
# netstat -ltup | grep zabbix_agentd
OR
# ss -ltup | grep zabbix_agentd
```
The fifth column shows the socket: Local Address:Port. In this case, the process **zabbix_agentd** is listening on port **10050**.