# NAT (Network Address Translation)
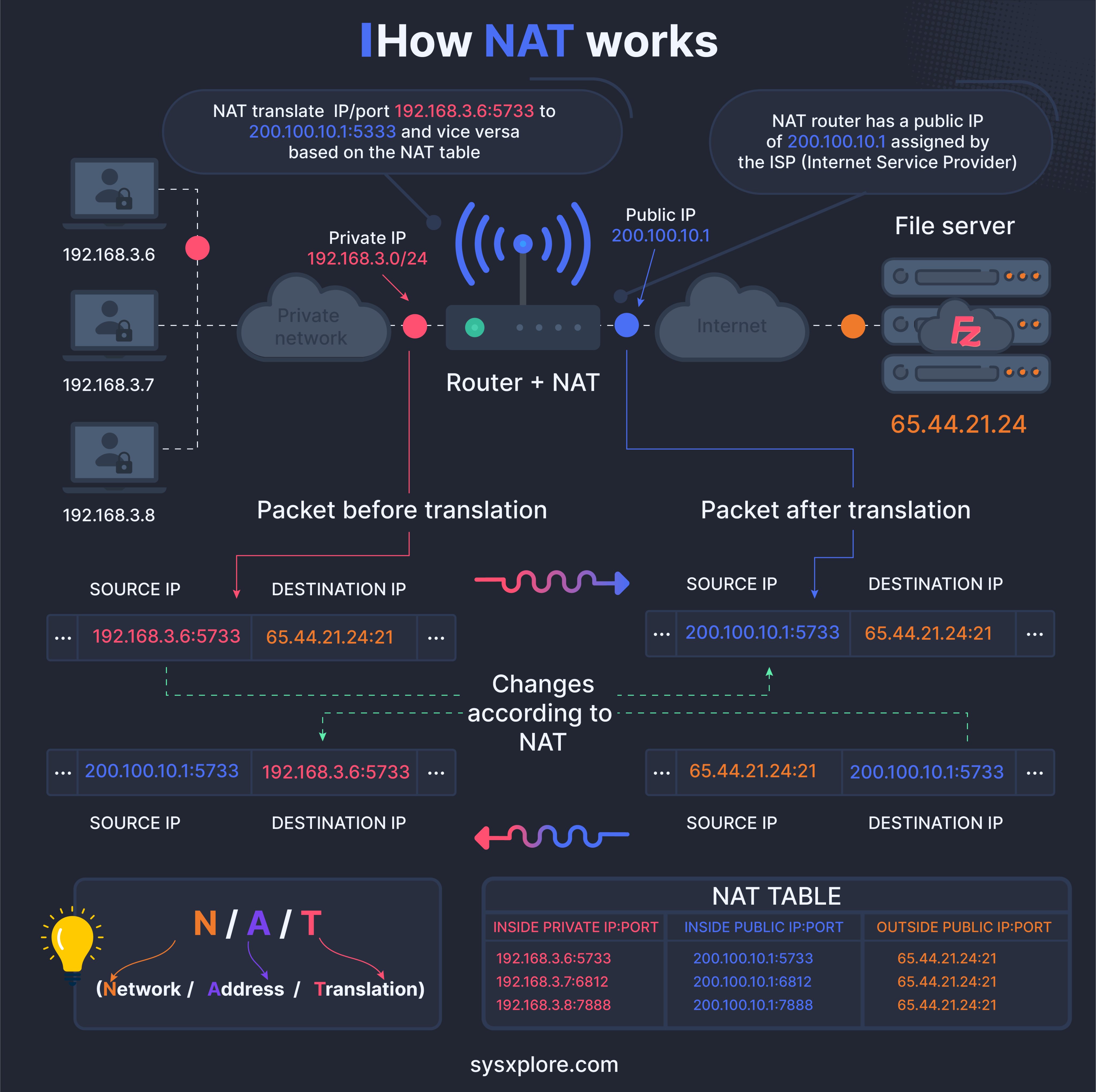
NAT stands for Network Address Translation. It is a method of mapping multiple private network addresses to a single public IP address before sending packets to the internet.
NAT is used to conserve IP addresses as IPv4 addresses are running out.
## How NAT Works
- For example, your computer's address in a local network might be 192.168.0.5.
- When you send a request to a server, the server cannot send a response to this address because it is not unique.
- NAT converts the private address to a public one.
- The request is sent to the server with a public address, the server replies to the public address, and NAT translates the response back to the private address within the local network.
## Types of NAT
- **Static NAT** — manual mapping of a private IP address to a public IP address.
- **Dynamic NAT** — automatic mapping of a private IP address to a public IP address.
- **PAT (Port Address Translation)** — mapping based on port numbers.
- **NAT Overload** — using a single public address to translate many private addresses.